读源码-String
String操作
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abCb";
System.out.println(str.length());
System.out.println(str.charAt(2));
System.out.println(str.getBytes());
System.out.println(str.equals("abc"));
System.out.println(str.equalsIgnoreCase("aBc"));
System.out.println(str.compareTo("bbb"));
System.out.println(str.contains("b"));
System.out.println(str.startsWith("a"));
System.out.println(str.endsWith("c"));
System.out.println(str.indexOf(0));
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf(0));
System.out.println(str.substring(1));
System.out.println(str.concat("d"));
System.out.println(str.replace("b", "B"));
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("b", "B"));
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str.trim());
System.out.println(str.split("b"));
}
}
String实现
String是不可变的,其是一个final类
public final class String
其实现了java.io.Serializable, Comparable
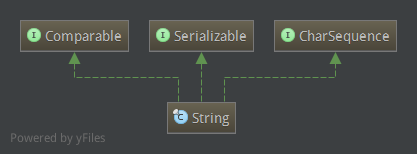
String是围绕char数组来实现和操作
private final char value[];
length()
length()方法即获取字符数组的长度
public int length() {
return value.length;
}
charAt()
charAt()方法,即是获取字符数组对应下标的值
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];
}
getBytes()
getBytes()方法,通过StringCoding实现
public byte[] getBytes() {
return StringCoding.encode(value, 0, value.length);
}
equals()
equals()方法,比较两个字符串对应的char数组是否相同
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String) anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
equalsIgnoreCase()
equalsIgnoreCase()方法,与equals()方法类似,只不过对每个char都调用了toUpperCase()方法
//核心方法在regionMatches中
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) {
return (this == anotherString) ? true
: (anotherString != null)
&& (anotherString.value.length == value.length)
&& regionMatches(true, 0, anotherString, 0, value.length);
}
compareTo()
compareTo()方法是Comparable接口中的方法,String中的实现如下:
//遍历每个char,根据对应的整形进行比较
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length;
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) {
char c1 = v1[k];
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) {
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;
}
return len1 - len2;
}
contains()
contains()方法实际上根据indexOf方法来进行判断:
static int indexOf(char[] source, int sourceOffset, int sourceCount,
char[] target, int targetOffset, int targetCount,
int fromIndex) {
if (fromIndex >= sourceCount) {
return (targetCount == 0 ? sourceCount : -1);
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
}
if (targetCount == 0) {
return fromIndex;
}
char first = target[targetOffset];
int max = sourceOffset + (sourceCount - targetCount);
for (int i = sourceOffset + fromIndex; i <= max; i++) {
/* Look for first character. */
if (source[i] != first) {
while (++i <= max && source[i] != first);
}
/* Found first character, now look at the rest of v2 */
if (i <= max) {
int j = i + 1;
int end = j + targetCount - 1;
for (int k = targetOffset + 1; j < end && source[j]
== target[k]; j++, k++);
if (j == end) {
/* Found whole string. */
return i - sourceOffset;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
startsWith()
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value;
int to = toffset;
char pa[] = prefix.value;
int po = 0;
int pc = prefix.value.length;
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
endsWith()
endsWith()是对startsWith()方法的委托调用
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, value.length - suffix.value.length);
}
indexOf()
indexOf()简单的遍历比较
public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
final int max = value.length;
if (fromIndex < 0) {
fromIndex = 0;
} else if (fromIndex >= max) {
// Note: fromIndex might be near -1>>>1.
return -1;
}
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
for (int i = fromIndex; i < max; i++) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
return indexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}
lastIndexOf()
lastIndexOf()与indexOf()类似
public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) {
if (ch < Character.MIN_SUPPLEMENTARY_CODE_POINT) {
// handle most cases here (ch is a BMP code point or a
// negative value (invalid code point))
final char[] value = this.value;
int i = Math.min(fromIndex, value.length - 1);
for (; i >= 0; i--) {
if (value[i] == ch) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
} else {
return lastIndexOfSupplementary(ch, fromIndex);
}
}
substring()
substring()通过截取对应长度的char数组,根据截取后的char数组构建一个新的String实现
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}
concat()
concat()构建一个长度为字符串总长度的字符数组,通过此数组构建一个新的字符串
public String concat(String str) {
int otherLen = str.length();
if (otherLen == 0) {
return this;
}
int len = value.length;
char buf[] = Arrays.copyOf(value, len + otherLen);
str.getChars(buf, len);
return new String(buf, true);
}
replace(),replaceAll()
replace(),replaceAll()通过正则表达式实现
public String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(target.toString(), Pattern.LITERAL).matcher(
this).replaceAll(Matcher.quoteReplacement(replacement.toString()));
}
public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) {
return Pattern.compile(regex).matcher(this).replaceAll(replacement);
}
toLowerCase(),toUpperCase()
toLowerCase(),toUpperCase()主要通过Character类中的方法实现,代码过长,不列出。
trim()
trim()通过比较空格字符来处理
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {
st++;
}
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}
split()
split()正则表达式实现
public String[] split(String regex, int limit) {
/* fastpath if the regex is a
(1)one-char String and this character is not one of the
RegEx's meta characters ".$|()[{^?*+\\", or
(2)two-char String and the first char is the backslash and
the second is not the ascii digit or ascii letter.
*/
char ch = 0;
if (((regex.value.length == 1 &&
".$|()[{^?*+\\".indexOf(ch = regex.charAt(0)) == -1) ||
(regex.length() == 2 &&
regex.charAt(0) == '\\' &&
(((ch = regex.charAt(1))-'0')|('9'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'a')|('z'-ch)) < 0 &&
((ch-'A')|('Z'-ch)) < 0)) &&
(ch < Character.MIN_HIGH_SURROGATE ||
ch > Character.MAX_LOW_SURROGATE)){
int off = 0;
int next = 0;
boolean limited = limit > 0;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while ((next = indexOf(ch, off)) != -1) {
if (!limited || list.size() < limit - 1) {
list.add(substring(off, next));
off = next + 1;
} else { // last one
//assert (list.size() == limit - 1);
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
off = value.length;
break;
}
}
// If no match was found, return this
if (off == 0)
return new String[]{this};
// Add remaining segment
if (!limited || list.size() < limit)
list.add(substring(off, value.length));
// Construct result
int resultSize = list.size();
if (limit == 0)
while (resultSize > 0 && list.get(resultSize - 1).length() == 0)
resultSize--;
String[] result = new String[resultSize];
return list.subList(0, resultSize).toArray(result);
}
return Pattern.compile(regex).split(this, limit);
}